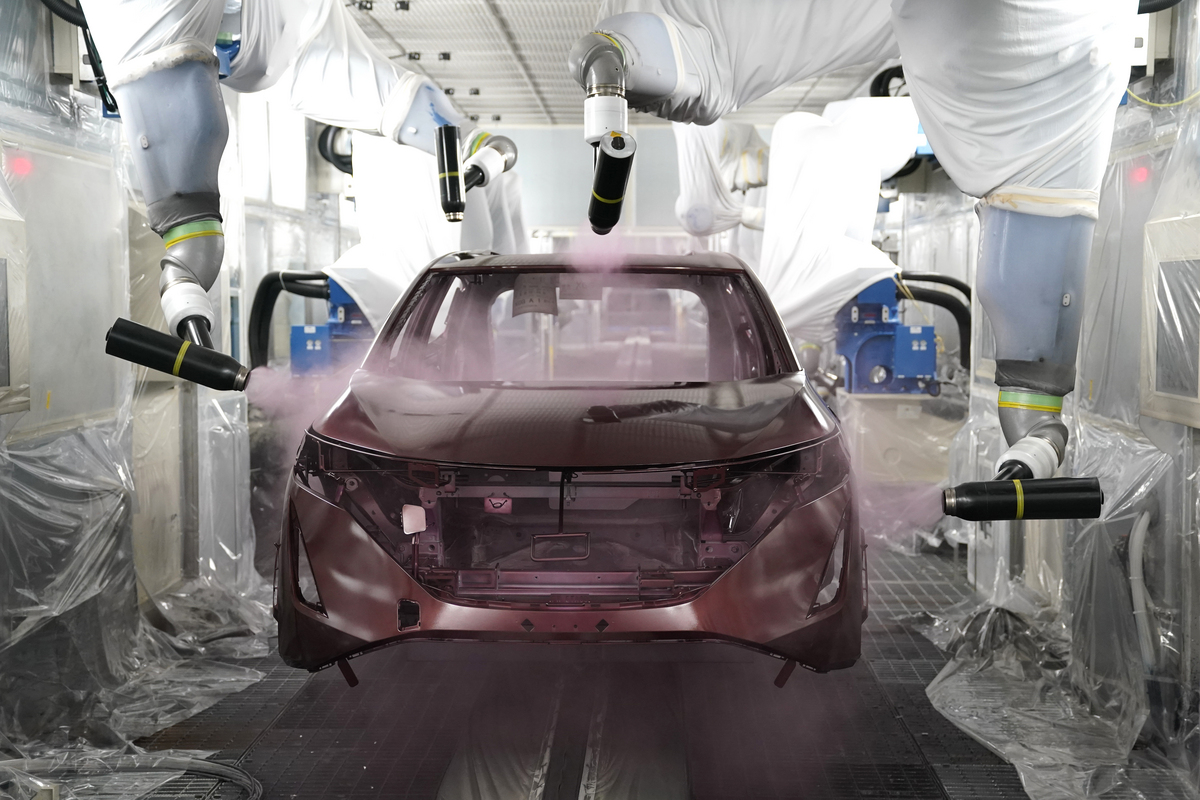
Nissan has announced plans to spend as much as $1.2 billion to implement new technologies at its factories around the world in an effort to make them more efficient and less polluting.
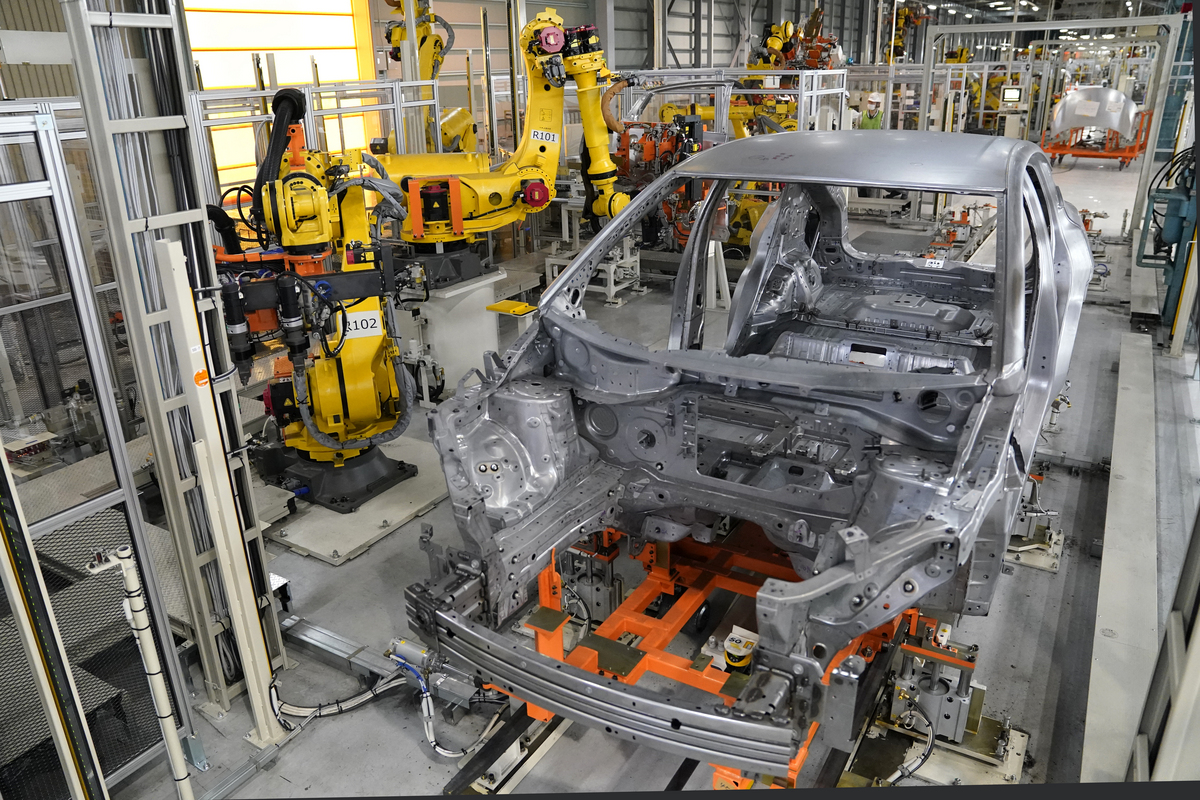
Known as their ‘Intelligent Factory Initiative’, Nissan has already spent nearly $300 million over the last two years to convert their Tochigi Plant with the new advanced equipment.
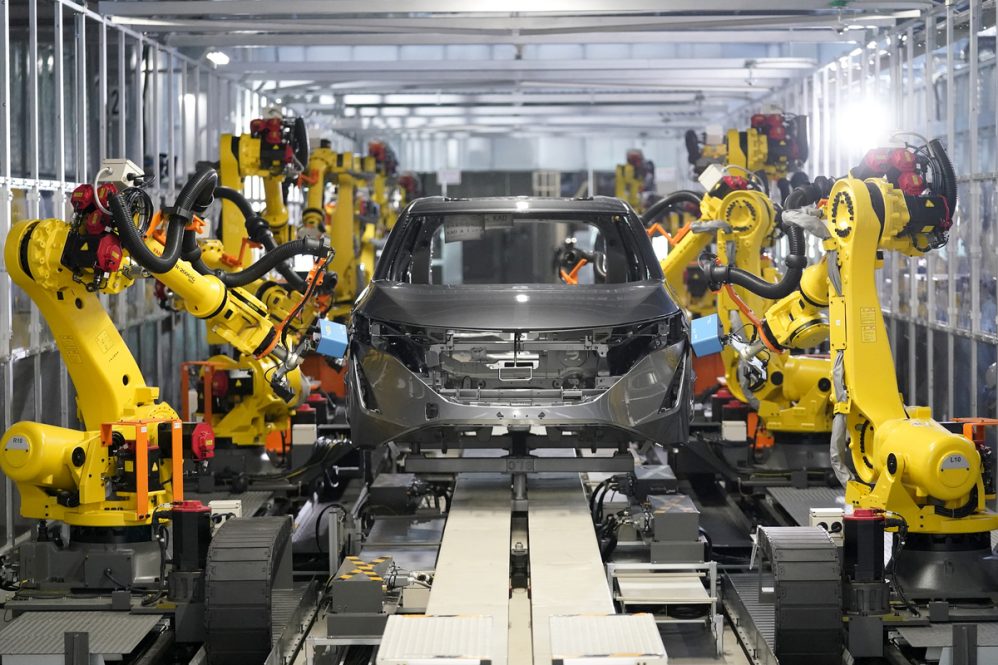
The factory will include production facilities for electric vehicles (EVs), including the new Ariya electric SUV that is set to debut in Japan later this year.
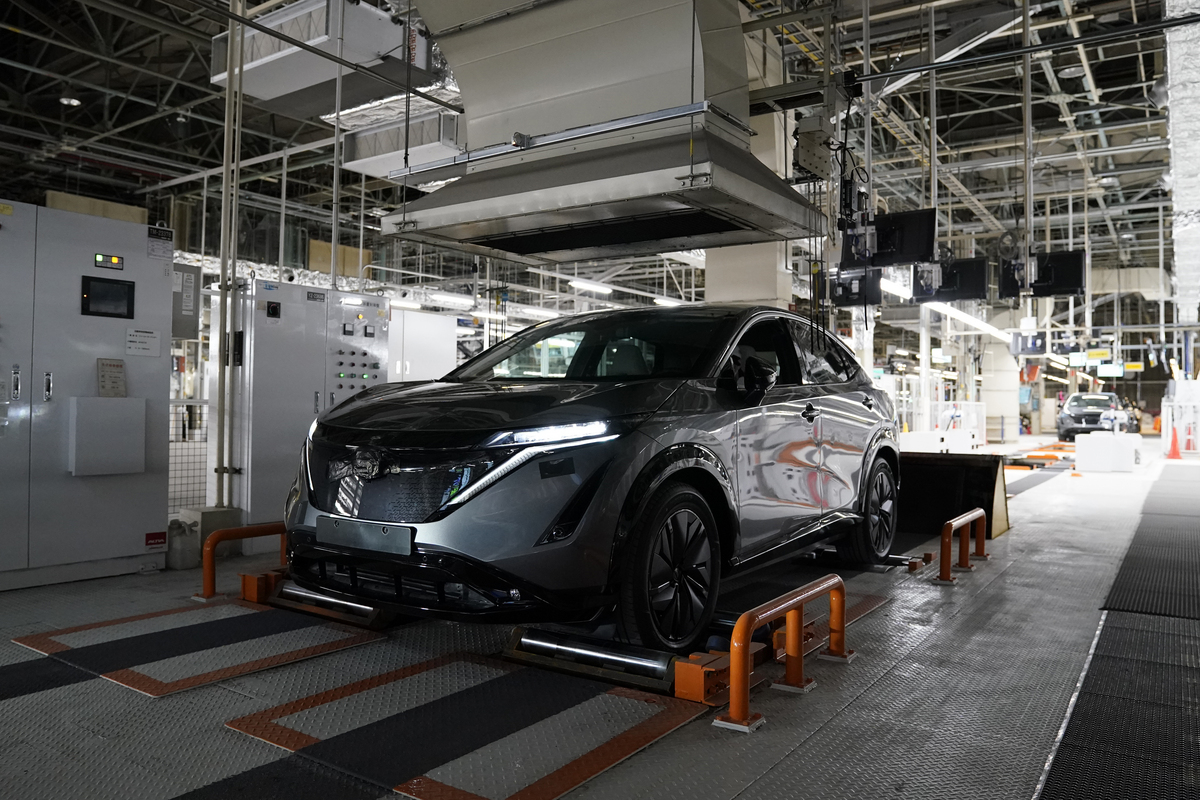

Since the Tochigi plant will also be producing internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, the equipment and lines have been modified to accommodate both vehicle architectures. For example, in the section of the production line which mounts the different powertrains, the new intelligent systems measure the car’s dimensions and makes micro-adjustments on the fly to ensure everything is installed to within less than a millimeter of accuracy.
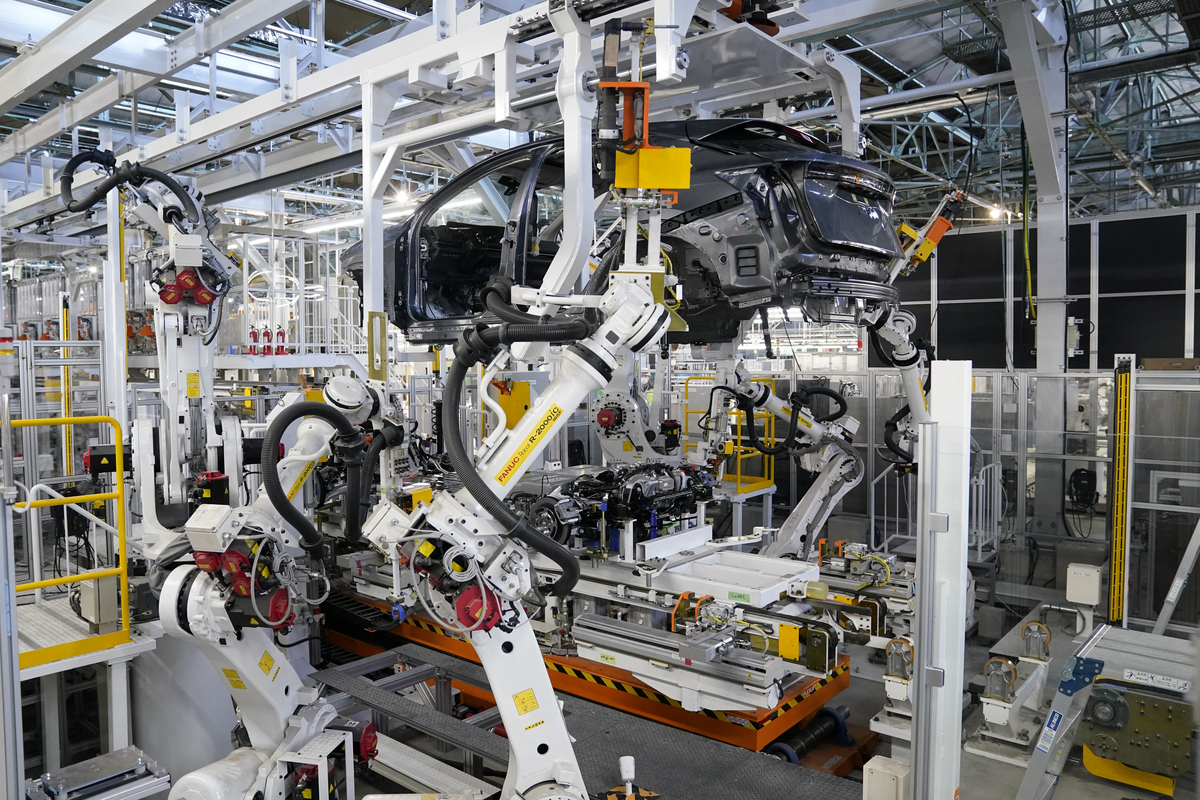
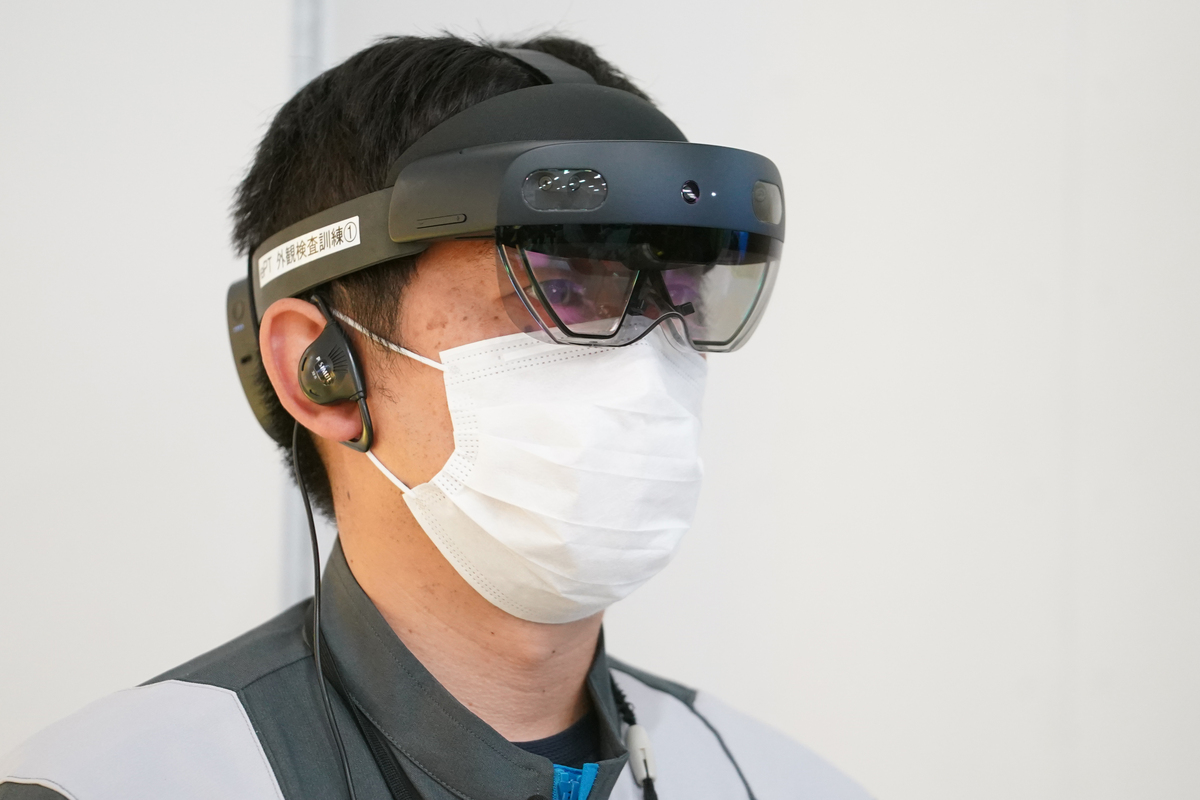
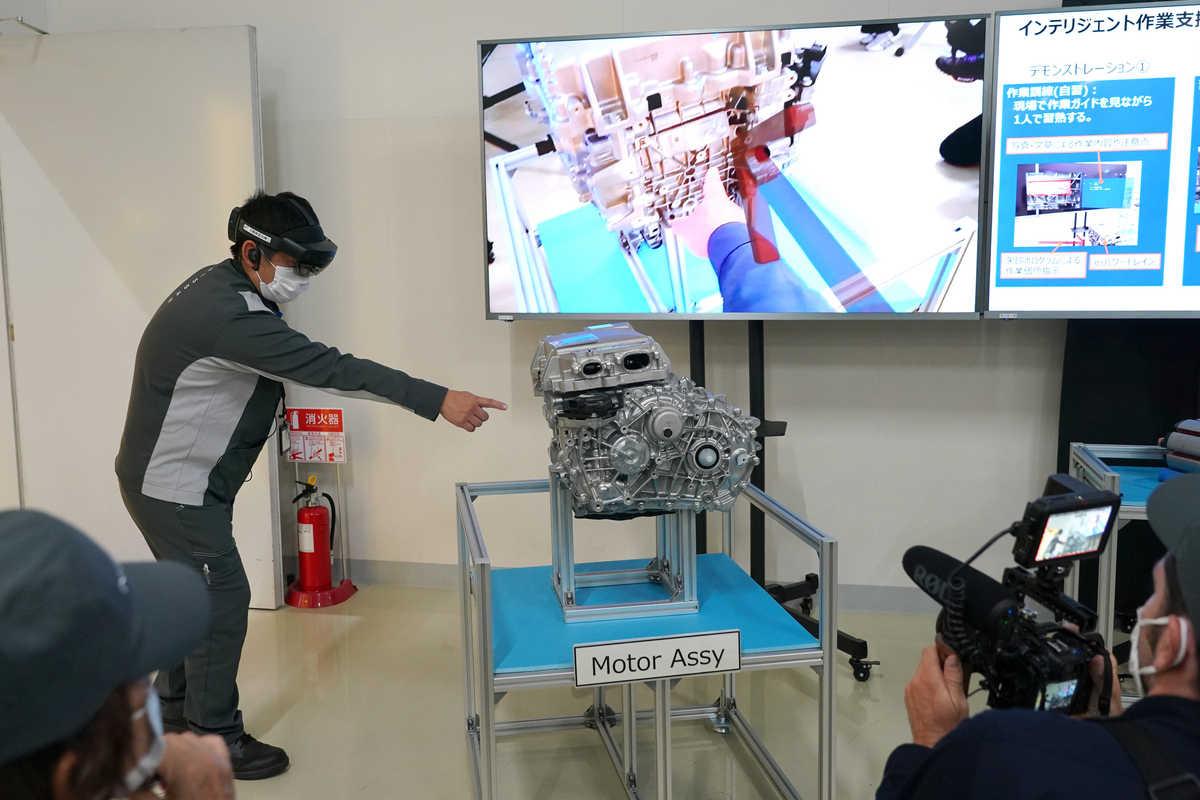
The changes don’t just impact the robots, but also the people that work on the lines. To increase efficiency, workers have mixed-reality headsets that are used for training and to complete quality control inspections.
When looking at parts with the headset on, instructions appear and arrows point to sections that need to be inspected. A walk-around of a virtual car can also be performed.
After converting the Tochigi plant, which produces around 255,000 vehicles per year, the automaker will now focus on other plants in Oppama and Kyushu, before moving on to its factories in the United States.
Through the initiative, Nissan is aiming to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 at its production facilities around the world.
“The automotive industry is in a period of great change, and solving the global challenge of climate change is urgent. We see this as an opportunity to build the strength of monozukuri (manufacturing), a part of our DNA, to develop and apply innovative technologies to overcome the challenges we face,” said Hideyuki Sakamoto, Nissan’s executive vice president for manufacturing and supply chain management.













